
Enterprise Switch VS Data Center Switch VS Home Switch: What's the difference? How do I choose?
Date:2021-04-01Click:1162
Today, the switch is no longer proprietary to telecommunications, in the data center, enterprise network, home office and other places everywhere its shadow. Different usage scenarios require different switches, so there are data center switches, enterprise switches, home switches, and so on, where enterprise switch penetration is high, so what do you know about enterprise switches? What is the difference between an enterprise switch and a data center switch and a home switch? And how to choose? You'll find the answer by reading this article.
What is an enterprise switch?
An enterprise switch is an Ethernet switch that provides data forwarding for fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, and 10G Ethernet, with management and operational configuration features such as CLI, Web, and SNMP (such as display, modification, backup, and restore). In general, enterprise switches are rack-mounted switches that support more than 500 points of information when it is the backbone switch.
An overview of enterprise switch types
According to the three-tier network structure model, enterprise switches can be divided into access layer switches, aggregation layer switches, and core layer switches. Among them, the access layer switch is equivalent to the company's structure of the grass-roots staff, mainly for wireless AP, computer, IP camera and other terminal equipment to provide network connectivity, convergence layer switch is equivalent to the company structure of the middle-level management, is the convergence point of multiple access layer switches, mainly used to aggregate all the communication of the access layer switch and provide to the uplink, the core switch is equivalent to the company structure of the management level, is the hub of the network, It mainly provides a fast and reliable backbone transmission structure through high-speed forwarding communication.
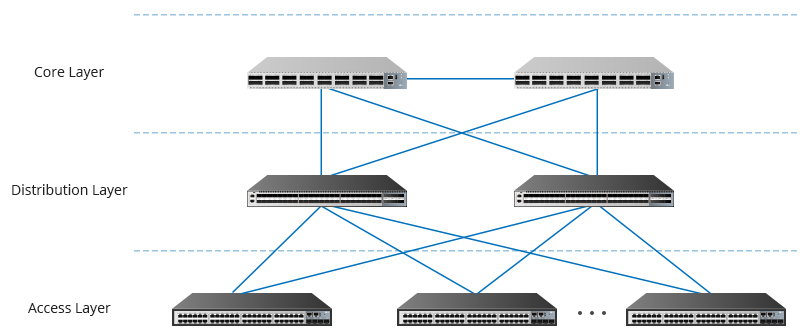
| The comparison item | Access layer switch | Convergence layer switches | Core layer switches |
|---|---|---|---|
| The work layer | Access layer | Convergence layer | The core layer |
| characteristic | Two-tier switch Low reliability Low functionality Low throughput | Two- or three-tier switches are highly reliable, highly functional, high throughput | The three-tier switch has the highest reliability, the highest functionality, and the highest throughput |
| The number in the network architecture | More | In general, it is between the other two switches | Less (usually one or two) |
| function | Access control, security management, VLAN, Ethernet power, etc | Packet filtering, QoS, etc | QoS, redundant components, etc |
| cost | low | high | highest |
| Switch type | For example, gigabit switches | For example, a 100-megabit switch | For example, 25G/40G/100G switches |
What's the difference between an enterprise switch, a data center switch, and a home switch?
The above is from the enterprise network switch itself, the next enterprise network switch and data center and home office switch comparison, in order to better understand the enterprise network switch. So what's the difference between a data center switch, an enterprise switch, and a home switch?
First, the three connect different objects. In general, data center switches are primarily used to connect servers or IP storage, such as the high-performance N-Series switches introduced by Cisco, home switches are primarily used to connect routers, and enterprise-class switches are primarily used to connect wireless AP, IP cameras.
Secondly, there is a big difference between the functions of the three. Among them, data center switches are complex and powerful, and home switches are the simplest.
Because data centers require higher density and bandwidth, and require business-accurate identification and control capabilities, data center switches typically use technologies such as large cache, virtualization, FCOE, TRILL (sophomore layer), higher density and bandwidth, and higher quality business and control identification capabilities to respond quickly and without losing packets, ensuring business continuity and system reliability. At the same time, data centers are transforming a three-tier network architecture into a spinal network architecture in response to future bandwidth growth, with ridge switches at the heart of the network architecture and leaf switches providing network connectivity for servers, among others.
In the enterprise network, because of the diversity of access equipment, both wired and wireless devices, such as printers, IP phones, computers and other equipment, so enterprise switches will generally use PoE, MPLS, QoS, VPN, etc., with a higher security management capabilities, each access device to achieve tracking and monitoring management, to ensure the security and reliability of the network.
Home office is usually no more than 10 people, so most people choose a fool switch as a home, simple function, no network management function, just communication can be. In a home office network, a home switch is equivalent to simply extending the router's ports and increasing the number of access users. And because home switches are plug-and-play when used, there is no configuration management, relatively low cost.
Finally, there are price differences between the three. In general, the price of data center switches is > the price of enterprise switches > the price of home switches.
Should enterprises choose a data center switch or an enterprise switch?
In the network architecture, the performance of the switch as the core network device affects the performance of the network, so switch selection is very important. From above, enterprise switches and data center switches are rich in functionality, so how should enterprises make choices? Consider this in the following ways. as
Whether you need extra capacity backplane bandwidth and wire-speed forwarding rates, select a data center switch if needed, and meet the requirements if the requirements are not particularly high for an enterprise-class switch.
Whether virtualization is required to unify the management of multiple network devices, if you need to choose a data center switch, if there are few network equipment, no unified management, choose an enterprise switch.
Whether strong network management capabilities are required, and if it is simple VLAN-to-Vlan communication, priority queue services, and network security controls, enterprise-class switches are generally sufficient. In addition to requiring it to have a variety of advanced network protocols such as routing protocol/ACL/QoS/load balancing, FCOE, TRILL and other functions are required, then it is more appropriate to choose a data center switch.
Whether you need to support multiple businesses, such as voice, video, data, and so on, is appropriate if you need to choose an enterprise switch.
In any case, businesses must start with their own network needs, the most "beautiful" price to buy a good performance and meet the needs of the switch is the most critical.
summary
Some models of Cisco are listed below for your simple comparison
Data center switch:
Nexus 9500 Series Switches, Modular, 1/10/25/40/50/100 G port types, 60 Tbps switching capacity, NX-OS, ACI
Nexus 9500 R-Series Switches, Modular, 1/10/25/40/50/100 G port types, 60 Tbps switching capacity, NX-OS only
Nexus 9300 Series Switches, Modular, 1/10/25/40/100 G port types, 1.44 to 2.56 Tbps switching capacity, NX-OS, ACI
Nexus 3000 Series Switches, Fixed, 1/10/25/50/100 G port types, 176 Gbps to 6.4 Tbps switching capacity, NX-OS
MDS 9718 Multilayer Director, Modular storage, 10/40 G FCoE, 2 to 32Gbps autosensing FC port types, 18 Tbps Fibre Channel switching, MDS NX-OS
Nexus 2300 Series Fabric Extenders, Fixed, 1/10 G port types, 80 to 240 Gbps switching capacity, NX-OS, ACI
MDS 9710 Multilayer Director, Modular storage, 10/40 G FCoE, 2 to 32 Gbps autosensing FC port types, 12 Tbps Fibre Channel switching, MDS NX-OS
CompareMDS 9706 Multilayer Director, Modular storage, 10/40 G FCoE, 2 to 32 Gbps autosensing FC port types, 6 Tbps Fibre Channel switching, MDS NX-OS
MDS 9396T 32G Multilayer Fabric Switch, Fixed fabric, 4 to 32 Gbps autosensing FC port types, 3 Tbps Fibre Channel switching, MDS NX-OS
CompareMDS 9148T 32G Multilayer Fabric Switch, Fixed fabric, 4 to 32 Gbps autosensing FC port types, 1.5 Tbps Fibre Channel switching, MDS NX-OS
CompareMDS 9132T 32G Multilayer Fabric Switch, Fixed fabric switch, 4 to 32 Gbps autosensing FC port types, 1 Tbps Fibre Channel switching, MDS NX-OS
CompareMDS 9250i Multiservice Fabric Switch, Fixed fabric switch, 2 to 16 Gbps, autosensing FC port types, 740 Gbps Fibre Channel switching, MDS NX-OS
With the above details, I believe you have a better understanding of enterprise switches, can distinguish between enterprise switches, data center switches and home switches, and make the right choices.

